Vaping THC, a common method of consuming cannabis, raises questions about its duration in the body. Understanding how long THC stays in the system is important for various reasons, including health considerations, legal implications, and preparation for drug tests.
This blog post delves into various aspects of Tetrahydrocannabinol, from its basic definition to the factors affecting its stay in the body, along with detection methods and tips for speeding up its clearance.
What is THC?
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, known for causing the ‘high’ sensation. It’s found in cannabis plants and works by interacting with brain receptors, affecting mood, consciousness, and perception.
The effects of Tetrahydrocannabinol can vary greatly, ranging from euphoria and relaxation to anxiety and paranoia, largely dependent on the dose and individual response. THC’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system in the brain plays a crucial role in these varied effects, making it a compound of interest both for recreational use and scientific study.
Understanding Tetrahydrocannabinol is key to comprehending its impact on the body and the duration of its effects.
Vaping THC ─ How it Works

Vaping THC involves inhaling vaporized cannabis oil, a method that has gained popularity for its convenience and perceived health benefits over traditional smoking. When inhaled, Tetrahydrocannabinol is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream through the lungs, leading to a quick onset of effects.
This method of delivery makes vaping an attractive option for those seeking immediate relief or a quick psychoactive experience. However, this also means that THC reaches detectable levels in the body very quickly after use.
Vaping’s efficiency in delivering Tetrahydrocannabinol to the bloodstream highlights its appeal but also raises concerns regarding overconsumption and the management of its effects.
Factors Affecting THC Stay in Your System
The duration THC stays in your system is influenced by several factors. The frequency of use is crucial; regular users will have Tetrahydrocannabinol detectable in their systems for longer periods compared to occasional users.
Dosage also significantly affects how long THC stays detectable; higher doses typically lead to longer retention times. Individual differences such as metabolism, body fat percentage, and overall health condition play critical roles in how Tetrahydrocannabinol is processed and eliminated.
These factors combine to make it difficult to precisely predict the duration of THC’s presence in any individual’s system even if you’re using https://trehouse.com/collections/magic-mushroom-gummies/.
Detection Methods
Detecting THC in the body is done through several methods, each with its own detection timeline. The most common tests include urine, blood, and hair follicle tests. Urine tests are popular for their ease of use and ability to detect Tetrahydrocannabinol metabolites for an extended period after consumption.
Blood tests, though more invasive, are effective in detecting active THC, which indicates recent use.
Hair follicle tests have the longest detection window, capable of revealing Tetrahydrocannabinol use over several months. Each of these methods provides valuable information in different contexts, from medical examinations to legal screenings.
How Long Does THC Stay in Urine?
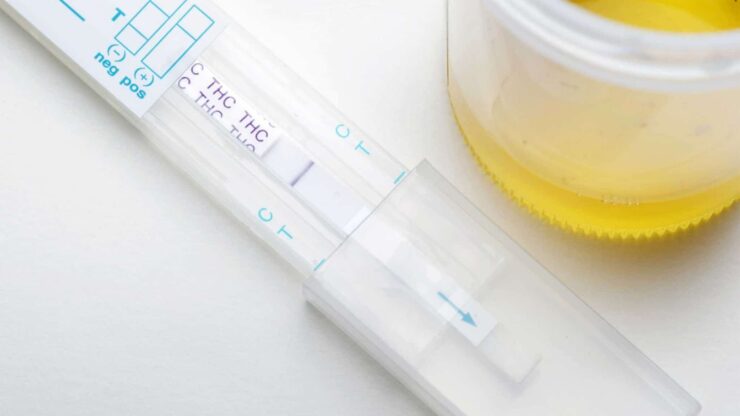
THC’s detectability in urine varies based on several factors, including usage patterns and individual differences. For occasional users, THC is generally detectable in urine for a few days. However, for regular, heavy users, this period can extend to weeks or even months.
The process of Tetrahydrocannabinol metabolism, where it’s broken down into metabolites detectable in urine, and the sensitivity of the testing method play significant roles in determining the detection timeframe. This variability makes it challenging to provide a one-size-fits-all answer for Tetrahydrocannabinol’s duration in urine.
THC in Blood ─ Duration of Detection
The detection window for THC in blood is relatively brief. It’s typically detectable for a few hours to a couple of days, reflecting the body’s rapid metabolism and elimination of Tetrahydrocannabinol from the bloodstream.
Blood tests, therefore, are more indicative of recent THC use rather than long-term consumption patterns. This short detection window in blood tests is crucial for situations where understanding recent consumption is vital, such as in roadside sobriety tests or acute medical assessments.
Hair Follicle Testing
Hair follicle testing provides a long-term view of Tetrahydrocannabinol use, capable of detecting drug use over several months. THC metabolites enter the hair follicles through the bloodstream, and these traces remain as the hair grows out.
Despite its extended detection window, hair testing has limitations, such as its inability to pinpoint the exact timing of use and the potential for external contamination affecting test results. Nevertheless, this method is widely used in employment screening and legal contexts where long-term drug use history is relevant.
Saliva Testing
Saliva testing offers a brief detection period for THC, usually lasting up to 24-48 hours post-use. Its non-invasive nature and rapid results make it a practical choice for roadside testing and immediate post-accident investigations.
The detection window in saliva tests can be influenced by various factors, including the method of Tetrahydrocannabinol consumption and the individual’s metabolic rate. This testing method is particularly useful in situations requiring a quick assessment of recent drug use.
THC Half-Life

The half-life of THC is a vital concept in understanding its duration in the system. It refers to the time required for half of the drug to be eliminated from the body. THC’s half-life varies among individuals, influenced by factors such as frequency of use, body composition, and metabolic rate.
This variability in half-life is a crucial aspect in estimating how long Tetrahydrocannabinol might remain detectable in the system, helping to inform both users and health professionals about the dynamics of THC metabolism.
Tips for Speeding Up THC Clearance
Several practices can help expedite the clearance of THC from the system. Staying well-hydrated aids in flushing out toxins, while regular exercise can boost metabolism, facilitating the elimination of Tetrahydrocannabinol.
A healthy diet, rich in fiber and essential nutrients, supports the body’s natural detox processes. These methods, however, do not guarantee rapid elimination, particularly for frequent Tetrahydrocannabinol users, and their effectiveness can vary based on individual health and lifestyle factors.
Conclusion
In summary, the duration of THC in the body depends on various factors, including usage patterns, personal health, and the type of test used for detection. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed decisions about Tetrahydrocannabinol use and preparing for potential drug tests.
While methods to expedite THC clearance exist, they are not foolproof, emphasizing the need for awareness and responsibility in Tetrahydrocannabinol consumption.
Related Posts:
- How to Make THC Vape Juice ─ Tips and Tricks for Beginners
- How Long Does It Take to Register a Company in the…
- What Is JIT Access? Tips and Insights for a Secure System
- Rat-Proofing Your Home - 9 Best Long-Term Solutions
- 13 Legal Tips for Overcoming Long-Term Disability…
- Admissions Essay Writing: Tips for Deciding How Long…












