Oxygen, essential for our bodies, plays a pivotal role, particularly during sleep. Adequate oxygen levels ensure our organs function optimally, contributing to restful, rejuvenating sleep. Conversely, low oxygen levels during the night can lead to various health complications, including daytime fatigue, headaches, and more severe conditions such as cardiovascular issues and cognitive impairments.
Understanding the importance of maintaining optimal oxygen levels while sleeping is therefore crucial for overall health and well-being. This guide aims to provide practical advice on improving oxygen intake during sleep, enhancing both sleep quality and general health.
Know Your Oxygen Levels
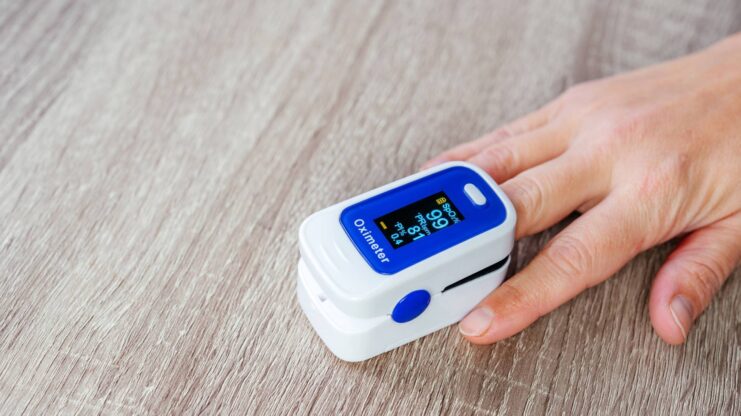
Measuring oxygen levels during sleep is crucial for understanding and improving your sleep health. A pulse oximeter, a small and convenient device that clips onto your finger, can help in this regard. Normal oxygen saturation levels fall between 95-100%, but dipping below this range during sleep can signal underlying health issues.
By regularly monitoring these levels, you can become more aware of your sleep patterns and potential problems. Additionally, understanding factors that influence oxygen levels, such as room environment and personal health conditions, can help you take proactive steps to ensure optimal oxygenation every night.
Sleep Positions Matter
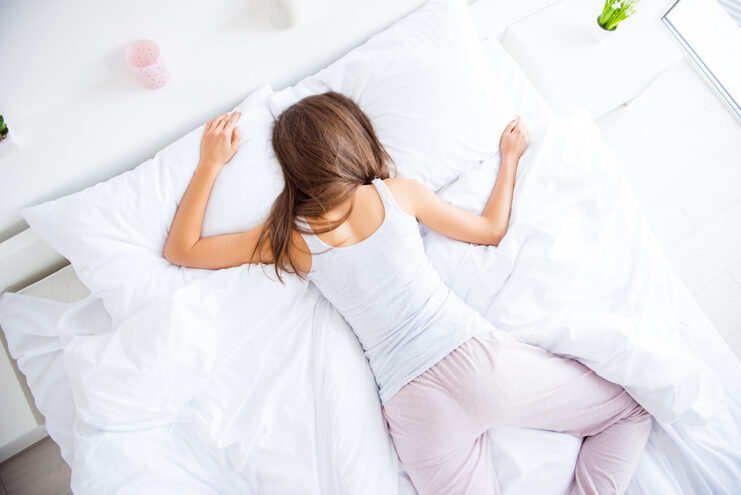

Your sleep position has a significant impact on your oxygen intake. For instance, sleeping on your back can sometimes obstruct airways, especially in individuals with conditions like sleep apnea. Side sleeping, particularly on the left side, is often recommended as it promotes better circulation and breathing.
Elevating the head with pillows can also aid in opening airways and improving oxygen flow. It’s essential to experiment with different sleep positions, and even consider specially designed pillows or mattresses, to find what significantly improves your breathing and oxygen levels during sleep. To sleep better straight away you should read more.
Room Ventilation
Proper ventilation in your bedroom plays a vital role in ensuring good air quality, which directly affects oxygen levels. An adequately ventilated room provides a continuous supply of fresh air, which is crucial for breathing well throughout the night.
Simple steps like keeping windows open when weather permits or using mechanical air purifiers can significantly improve the quality of the air you breathe. Additionally, it’s important to regularly clean and replace air filters in heating and cooling systems to maintain a clean, healthy sleeping environment conducive to optimal oxygen levels.
Humidity Control

The role of humidity in maintaining comfortable breathing conditions during sleep is often underestimated. Air that is too dry can irritate respiratory passages, while overly humid air can foster the growth of mold and allergens, leading to breathing difficulties.
Striving for a bedroom humidity level between 40-60% is ideal. Using tools like a hygrometer to monitor your room’s humidity, and employing humidifiers or dehumidifiers accordingly, can help in achieving this balance, thus facilitating easier breathing and better oxygenation during sleep.
Avoid Smoking and Secondhand Smoke
The detrimental effects of smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke on oxygen levels and lung function cannot be overstated. These habits not only reduce oxygen levels in the blood but also impair lung capacity, making it harder to breathe deeply while sleeping.
Quitting smoking and avoiding environments with secondhand smoke are critical steps in improving not only your nighttime oxygen intake but also your overall respiratory health. Moreover, these changes can lead to significant improvements in sleep quality and a reduction in the risk of developing chronic respiratory conditions.
Allergen Management

Allergens in the sleeping environment, such as dust, pet dander, and pollen, can significantly obstruct breathing during sleep. To combat this, consider using hypoallergenic bedding, regularly cleaning and vacuuming your sleeping area, and possibly using air purifiers to reduce the presence of allergens.
Additionally, keeping pets out of the bedroom and using allergy-proof covers on mattresses and pillows can further help minimize allergen exposure. Effectively managing these allergens is crucial for ensuring smoother breathing, leading to better sleep quality and increased oxygen levels.
Stay Hydrated
Hydration plays a critical role in maintaining healthy respiratory function. Adequate fluid intake helps in thinning mucus in the airways, facilitating easier breathing. It’s essential to drink sufficient water throughout the day, but it’s equally important to balance this with the need to avoid excessive fluid intake immediately before bedtime to prevent disruptive nighttime awakenings.
Maintaining good hydration levels not only supports better breathing but also contributes to overall health and well-being.
Regular Exercise

Engaging in regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to enhance lung capacity and improve overall respiratory health. Activities like brisk walking, swimming, yoga, and other aerobic exercises strengthen the respiratory muscles, leading to better breathing efficiency.
These exercises, when incorporated consistently into your routine, can significantly impact your nighttime oxygen levels, enhancing both sleep quality and lung function. Exercise also contributes to better stress management and overall physical health, which indirectly supports healthy sleep patterns.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
There’s a notable connection between obesity and sleep-related breathing issues such as obstructive sleep apnea. Excess weight can lead to obstructed breathing pathways, making it more difficult to maintain optimal oxygen levels during sleep.
Focusing on a balanced diet and regular exercise regime is key to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. This not only reduces the risk of sleep-disordered breathing but also enhances general health, improves sleep quality, and ensures more efficient oxygen intake at night.
Breathing Techniques

Incorporating simple breathing exercises into your daily routine can have a profound effect on improving lung capacity and oxygen intake. Techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing, which involves deep, rhythmic inhalation and exhalation using the diaphragm, can be particularly beneficial.
Regular practice of these techniques can help in maximizing lung function and enhancing the amount of oxygen absorbed during sleep, leading to better overall respiratory health and sleep quality.
Consult a Doctor
Persistent breathing issues during sleep warrant consultation with a healthcare provider. A medical professional can offer personalized advice and treatment options for conditions that may be affecting your breathing. This step is crucial, especially for those experiencing symptoms of sleep apnea or other respiratory issues